Technology now plays a central role in the way businesses operate, regardless of size. For small businesses, technology decisions can impact daily tasks, communication, and even customer relationships. The digital tools and services a business uses can influence how quickly it grows and how well it adapts to change.
Many people use the term “IT services,” but the meaning is not always clear. Some think of IT as fixing computers, while others see it as managing everything technical in a company. In reality, IT services include a wide range of support, from basic troubleshooting to planning for the future.
Understanding what IT services are—and how they work for small businesses—can help clarify what is involved in keeping technology running smoothly.
What IT Services Actually Mean for Small Businesses
Managed IT services work like a subscription where another company watches over your computers, software, and networks. They fix problems before they happen, keep everything updated, and help plan what technology to use next. This differs from the old way of calling someone only when something breaks.
Cloud solutions let businesses use software and store files on the internet instead of buying expensive servers. Companies can add or remove features as they grow without purchasing new equipment each time.
Cybersecurity support protects business data from hackers and viruses. This includes watching for attacks, responding when something goes wrong, and making sure the business follows data protection rules.
Key terms that come up often:
- MSP (Managed Service Provider): A company that takes care of another business’s computers and networks from a remote location
- SLA (Service Level Agreement): A written promise about how fast problems get fixed and how often systems stay running
How Technology Services Speed Up Growth
Strong computer systems help businesses launch new products faster and serve customers without crashes or slowdowns. When systems work reliably, companies can handle more customers and enter new markets without worrying about their technology failing.
Automation handles repetitive tasks that employees used to do manually. Software can now schedule appointments, send invoices, and organize customer information automatically. This frees up workers to focus on tasks that require human creativity and judgment.
Data analytics collects information from different parts of a business and puts it in one place. Instead of guessing what customers want or how much inventory to order, business owners can look at actual numbers and trends to make better decisions.
Digital transformation creates new ways for businesses to make money and connect with customers. Online stores, mobile apps, and digital payment systems help companies reach more people and adapt when industries change.
Essential Services That Growing Businesses Use
Growing small businesses typically focus on four main areas of IT support that directly affect their ability to make money and serve customers effectively.
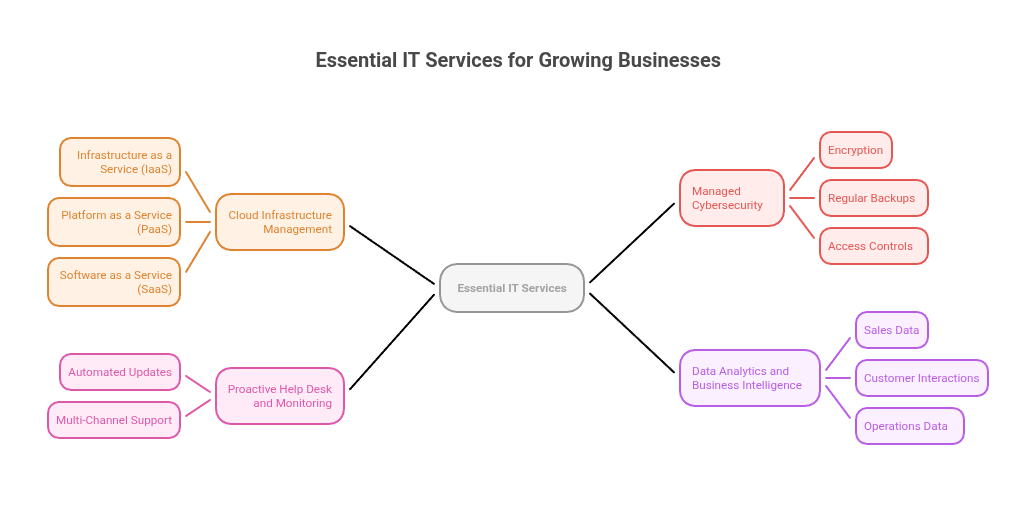
Cloud Infrastructure Management
Cloud infrastructure moves business data and software from physical computers to internet-based systems. Companies can access their files and programs from anywhere, scale up during busy periods, and support employees working from home.
The three main types are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Rents virtual servers and storage space
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Provides ready-made environments for building apps
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers finished programs through web browsers
Managed Cybersecurity
Managed cybersecurity involves continuous monitoring for threats, fixing security holes, and updating software to prevent attacks. When security incidents happen, response plans help businesses recover quickly and minimize damage.
Data protection methods include:
- Encryption: Scrambles data so only authorized people can read it
- Regular backups: Create copies of important files stored in separate locations
- Access controls: Limits who can view or change sensitive information
Proactive Help Desk and Monitoring
This service watches computer systems 24/7 to spot problems before they cause outages. Automated updates keep software current, and multi-channel support gives employees quick help when they encounter issues.
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
These tools collect information from sales, customer interactions, and operations to create dashboards showing how the business performs. Predictive analytics use historical data to forecast future trends, helping companies prepare for busy seasons or identify customers likely to cancel their services.
Measurable Results Business Owners See
IT services produce specific improvements that can be tracked and measured over time.
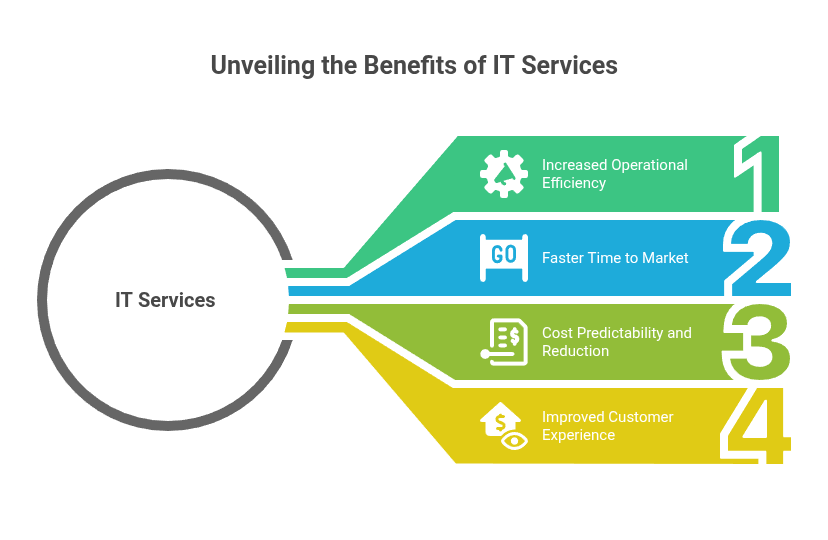
Increased Operational Efficiency
Streamlined workflows reduce the time it takes to complete routine tasks. Process automation eliminates repetitive manual work, while system integration connects different business applications so information flows smoothly between them.
Faster Time to Market
Automated testing and deployment tools help businesses develop and launch products more quickly. Teams can experiment with new features and make changes rapidly based on customer feedback.
Cost Predictability and Reduction
Fixed monthly fees for managed IT services replace unpredictable emergency repair costs. Businesses can operate with fewer in-house IT specialists, and optimized cloud usage eliminates waste from unused software licenses or excessive server capacity.
Improved Customer Experience
Reliable systems and faster response times increase customer satisfaction. Personalization tools and support across multiple channels help businesses engage customers more effectively throughout their relationship.
Comparing In-House vs Outsourced IT Costs
Businesses can either hire their own IT staff or work with external managed service providers. Each approach has different cost structures and benefits.
Direct vs Hidden Costs
In-house IT teams require salaries, benefits, and ongoing training costs. Hidden expenses include employee turnover, gaps in 24/7 coverage, and purchasing specialized tools and software licenses.
Managed services typically charge predictable monthly fees based on the number of users or devices. Most providers include tooling, updates, and round-the-clock coverage in their base pricing, minimizing unexpected costs.
Budgeting and Performance Tracking
Common pricing models include per-user rates, per-device fees, and tiered service levels. Businesses track performance using metrics like system uptime, average time to fix problems, and return on investment calculations tied to revenue per employee.
Security and Compliance for Business Growth
Strong security builds customer trust and enables partnerships with companies in regulated industries like healthcare and finance.
Threat Prevention Methods
Layered security defenses include endpoint detection tools, multi-factor authentication, and email security systems. These work together to reduce the likelihood of successful cyberattacks.
Regulatory Requirements
Businesses handling sensitive data follow specific compliance frameworks:
- HIPAA: Protects healthcare information privacy and security
- PCI DSS: Secures payment card data processing
- SOX: Ensures accurate financial reporting and controls
Meeting these requirements opens doors to new markets and partnerships while avoiding regulatory penalties.
Scaling Technology for Future Growth
Cloud computing and artificial intelligence provide flexibility to handle sudden increases in demand and adapt to new opportunities.
Elastic Resources
Auto-scaling automatically adds computing power during busy periods and reduces it when demand drops. Load balancing distributes work evenly across systems to maintain performance during traffic spikes.
Budget controls and rightsizing help businesses pay only for the resources they actually use.
Machine Learning Applications
ML algorithms identify patterns in large datasets to automate decision-making. Common applications include routing customer service inquiries, predicting inventory needs, and identifying customers at risk of canceling services.
Common Risks and Prevention Strategies
Technology transitions involve risks that can be reduced through careful planning.
Avoiding Vendor Lock-In
Vendor lock-in occurs when switching providers becomes difficult or expensive. Using open standards and portable architectures maintains flexibility. Contract negotiations can include data export rights and clear termination terms.
Preventing Service Disruptions
Service Level Agreements specify uptime guarantees and response times. Redundant systems and tested disaster recovery plans minimize the impact of outages. Regular backup testing ensures data can be restored when needed.
Selecting a Technology Partner
The right technology partner combines relevant experience with clear service commitments and a focus on supporting business growth.
Evaluation Criteria
Important factors include industry experience, technical certifications, security practices, and 24/7 support availability. Service Level Agreements outline expectations for system uptime and problem resolution times.
Key Questions for Potential Partners
- How do you secure endpoints, user accounts, and cloud resources?
- What is your average response time for different types of incidents?
- How do you handle data backups and disaster recovery testing?
- What services are included in monthly fees versus billed separately?
- Can you provide references from similar businesses in our industry?
NetTantra’s Approach to Business Technology
NetTantra Technologies specializes in AI, blockchain, and custom software solutions that help businesses automate processes, secure transactions, and build scalable platforms. Services include cloud architecture design, managed security, and digital transformation consulting aligned with specific business objectives.
For businesses ready to explore strategic IT services, proposal requests can be submitted at https://hyscaler.com/contact-us/business-enquiry/
FAQs About IT Services for Small Business Growth
What specific metrics show that IT services are actually driving business growth?
Revenue per employee typically increases while customer acquisition costs decrease, with measurable operational efficiency improvements usually visible within the first year.
How quickly do small businesses typically see a return on investment from managed IT services?
Most businesses notice productivity improvements within three months, with measurable cost savings and revenue growth becoming evident within six to twelve months.
Can small businesses start with basic IT services and add more advanced features later?
Most managed service providers offer scalable solutions that allow businesses to begin with essential services and gradually add capabilities as growth demands increase.
How do service level agreements actually protect small businesses from IT disruptions?
SLAs guarantee specific uptime percentages and response times, with financial penalties for providers who fail to meet these commitments, ensuring reliable service delivery.


Leave A Comment