Introduction
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital images, information, or 3D models onto real-world environments. It is visible through a smartphone, tablet, or AR glasses. AR is unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which transports you into a virtual world.
AR brings accountants closer to data. You don’t look down a list of numbers off a spreadsheet, but instead behold rich 3D reports. It is easier to analyze trends, to spot risk, and to be able to communicate results to clients.
Brief History and Evolution of AR
AR began in the 1960s as a tool for weapons and science. Its use grew with gaming and entertainment apps like Pokémon Go. In recent years, industries such as healthcare, retail, and construction have also adopted it.
Today, accounting is beginning to use AR as firms explore how it can improve productivity. Accountants deal with large datasets and complicated financial models. AR helps simplify these tasks by making data easier to understand and share.
Relevance of AR in the Modern Accounting Landscape
The accounting field is going digital. Cloud computing, AI, and blockchain are already changing how firms work. AR is now joining this list of tools.
Modern clients expect fast, clear, and visual financial reporting. AR allows accountants to present insights in engaging ways, which strengthens client trust. For firms looking to stay competitive, adopting AR may become more than an option—it could be a necessity.
Understanding the Use of Augmented Reality in Accounting
Current Applications of AR in Accounting
Accountants already deploy AR as part of everyday activity. Some firms use AR dashboards to project real-time finance data onto conference walls. It helps people work together better.
Accountants use AR to simulate financial operations. It helps trace transactions as well as identify mistakes. Tax professionals use AR to preview tax strategy impacts before implementation.
How AR Enhances Data Visualization
Numbers on spreadsheets can be overwhelming. AR condenses data by presenting it interactively with charts, 3D objects, or color-coded maps. You can immediately see trends or issues without having to read a long report.
Instead of a 50-page report, AR displays key financial risks or growth opportunities directly. This saves time and reduces errors.
Case Studies of AR in Accounting Practices
Several global firms have started experimenting with AR. For instance, Deloitte and PwC are exploring AR tools for auditing and training. Smaller firms are adopting AR-powered financial dashboards for client presentations.
A tax firm used AR to show real-time financial impacts of tax strategies to clients. This approach helped clients make more informed decisions and improved satisfaction.
The Benefits of Augmented and Virtual Reality in the Accounting Field
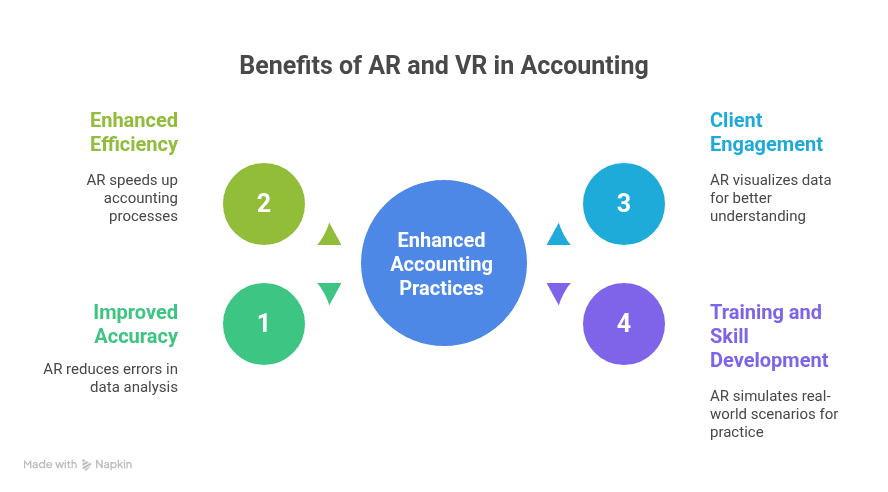
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
Manual data analysis often leads to errors. AR can cut these by making data checks faster and more reliable. Accountants can instantly visualize discrepancies that might otherwise go unnoticed.
By speeding up processes, AR helps firms reduce costs. For example, an audit that might take weeks can be completed more quickly with AR tools.
Enhanced Client Engagement and Communication
Explaining financial results can be difficult. With AR, you can walk clients through data in a visual format. This creates a better understanding and builds trust.
Clients value accounting insights more when visualized than in complex spreadsheets.
Better Training and Skill Development for Accountants
Training new accountants is expensive and time-consuming. AR allows firms to simulate real-world accounting scenarios. Trainees can practice audits, tax calculations, and compliance checks in a controlled environment.
This minimizes errors and prepares accountants for sensitive financial tasks.
How Augmented Reality is Changing Financial Reporting
Transforming Traditional Reporting Formats
Financial reports have long been text-heavy and difficult to read. AR enables interactive 3D financial charts and live data.
Instead of reading static numbers, clients and managers can interact with data. For example, they can explore sales performance by region with a simple gesture.
Interactive Dashboards and Real-Time Insights
AR-powered dashboards can update in real time as new data comes in. This helps decision-makers respond faster to financial changes.
Project your budget vs. spending on your office wall. This gives you instant clarity on whether targets are being met.
AR for Compliance and Audit Preparedness
Regulatory compliance requires thorough documentation and accurate reporting. AR can make compliance checks easier by visually flagging areas of concern.
Auditors can use AR to track audit trails more efficiently, saving time on document reviews. This helps firms prepare better for regulatory reviews.
Practical Examples of Augmented Reality in Accounting
Virtual Collaboration with Clients
AR enables virtual collaboration, even when accountants and clients are not in the same location. Furthermore, you can project financial dashboards during video meetings. This allows both parties to interact with the same data.
This eliminates misunderstandings and makes communication more productive.
AR in Tax Preparation and Planning
Tax planning often involves many scenarios. With AR, you can project different tax outcomes side by side. Clients can immediately see how choices impact their finances.
This leads to smarter decisions and greater client confidence.
AR Applications in Auditing
Auditors can use AR tools to map transaction flows across departments. This helps detect unusual activity and ensures better accuracy.
By visualizing the audit process, auditors save time and strengthen the reliability of their findings.
Comparing Augmented Reality with Traditional Accounting Tools
Differences in Efficiency
Traditional accounting tools rely on spreadsheets, static dashboards, and manual checks. These methods are time-consuming and prone to human error.
AR presents data visually and interactively. You can explore financial reports in 3D, making it easier to detect irregularities.
Efficiency improves when accountants use AR to automate repetitive tasks. For example, reviewing long financial statements becomes faster with AR, highlighting key areas. Compared to traditional tools, AR reduces manual effort and improves accuracy.
Cost Implications
Traditional accounting tools often need licensing fees and regular upgrades. AR may involve a higher initial investment, especially if firms need hardware like AR glasses.
But long-term savings come from improved efficiency and reduced errors. Fewer mistakes mean fewer penalties during audits or compliance checks.
Small and medium-sized firms may face budget challenges. Still, cloud-based AR applications are emerging, making the technology more affordable. In the long run, AR may prove cost-effective compared to traditional tools.
Adoption Challenges
Shifting from traditional tools to AR requires cultural and technical changes. Some accountants may resist because they feel comfortable with spreadsheets.
Additionally, training is required. Without proper training, staff may misuse AR features. Data security also becomes a concern when firms adopt new digital tools.
Despite these challenges, the transition is worthwhile. Firms that adopt AR early may gain a competitive advantage in the accounting industry.
The Future of AR and VR in Accounting
Predictions for AR Growth in the Finance Industry
AR adoption is expected to grow as more firms see its benefits. A growing number of accounting firms already test AR for data visualization and training.
Industry experts predict AR will become a standard tool in finance by the late 2020s. Firms that delay adoption may fall behind competitors.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain
AR’s real strength lies in integration. Imagine AR dashboards powered by AI detecting fraud in real time. Or combining AR with blockchain to track secure transactions visually.
This integration will create smarter, more reliable systems. Together, these technologies can transform how accountants analyze data and maintain trust.
Long-Term Impact on Accounting Jobs
Some worry AR will replace accountants. In reality, AR enhances, not replaces, their work. Routine tasks may become automated, but strategic decision-making still needs humans.
Accountants who adapt will shift toward advisory roles. They will spend less time on manual tasks and more on interpreting insights for clients.
Challenges of Implementing Augmented Reality in Accounting
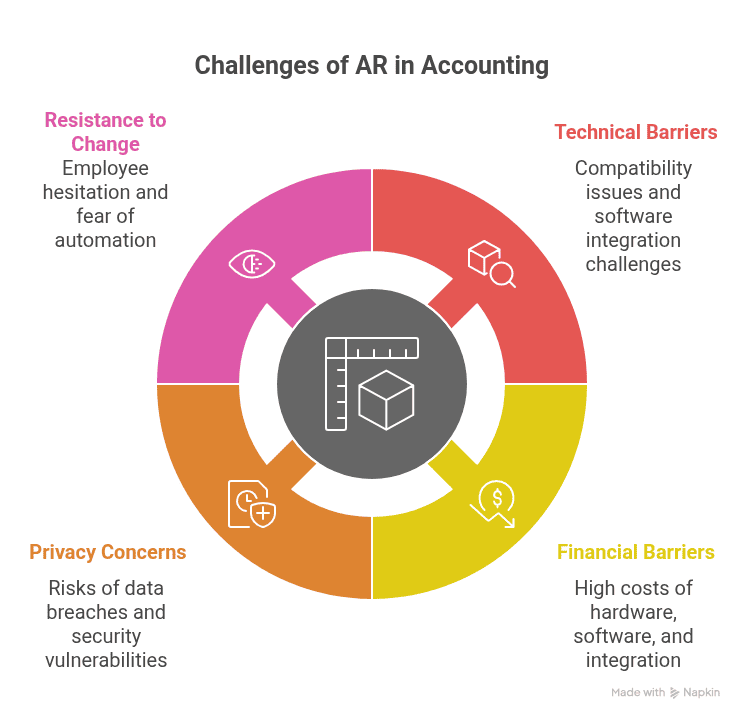
Technical and Financial Barriers
One of the biggest challenges is the cost of AR adoption. Firms must invest in hardware, software, and integration with existing systems.
Smaller firms may struggle with these costs, though cloud-based AR apps are helping reduce barriers.
Technical barriers include compatibility issues. Not all existing accounting software supports AR integration, which may slow adoption.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Accounting involves sensitive financial data. Storing and projecting this data through AR raises security risks. Firms must ensure strong encryption and access controls.
Hackers may target AR systems if protections are weak. Building robust cybersecurity measures is essential before adopting AR widely.
Resistance to Change
Employees may hesitate to use AR, fearing it is too complex. Others may worry that automation threatens their jobs.
Overcoming this resistance requires training and clear communication. Firms must show how AR benefits both clients and accountants.
Practical Steps for Adopting AR in Accounting Firms
Identifying the Right AR Tools
Not all AR tools suit accounting needs. Firms must assess software for compatibility, scalability, and ease of use.
Examples include AR dashboards for visualization or AR-enabled auditing platforms. Choosing the right tools prevents wasted investment.
Training Staff for AR Integration
Staff training is critical. Without proper training, accountants may fail to use AR effectively. Training should focus on both technical use and practical applications.
Some firms use AR-based training modules themselves, making onboarding more engaging.
Building a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Before adoption, firms should calculate whether AR will deliver real value. This includes considering efficiency gains, cost savings, and improved client relationships.
A clear cost-benefit analysis helps firms justify AR investments to stakeholders.
AR in Banking and Its Link to Accounting
AR in Customer Service
Banks already use AR to improve customer experiences. For example, AR apps help customers locate nearby ATMs or branches.
In accounting, similar tools may help clients access personalized financial insights in real time.
AR for Risk Management
Banks use AR to simulate risk scenarios. Accountants can apply the same technology to analyze risks in audits or investment portfolios.
By visualizing financial risks, AR helps firms make smarter, safer decisions.
AR for Personalized Financial Planning
Clients expect personalized services. With AR, accountants can create tailored financial plans. They can also show how different strategies affect long-term outcomes.
This level of engagement makes financial planning more interactive and client-focused.
Types of Augmented Reality and Their Relevance in Accounting
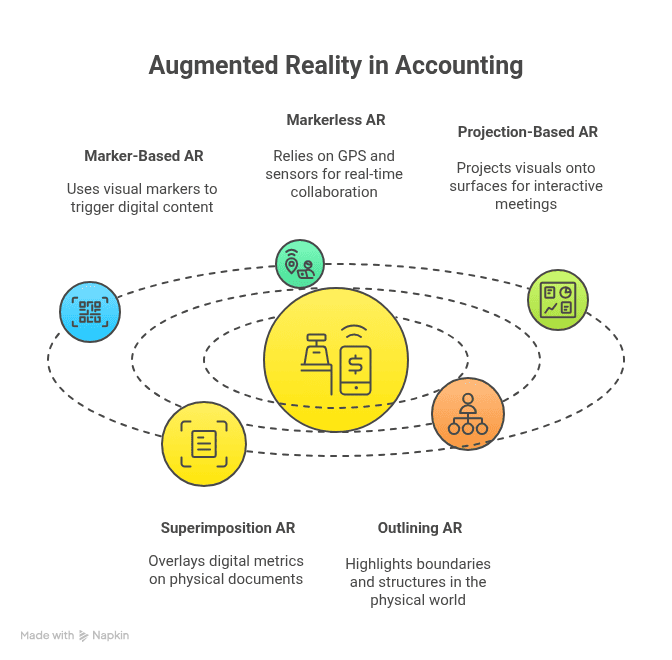
Marker-Based AR
Marker-based AR relies on a visual marker, like a QR code, to trigger digital content. In accounting, firms can use markers to pull up specific reports.
For example, scanning a marker on a client file might display their financial history. This makes retrieving information faster than searching through digital folders.
Markerless AR
Markerless AR uses GPS, accelerometers, and sensors instead of markers. For accountants, markerless AR could enable real-time collaboration with clients across locations.
Imagine pointing your phone at a client’s office building. You could immediately see their financial status. This type of AR allows more flexibility than marker-based tools.
Projection-Based AR
Projection-based AR projects visuals onto surfaces. Firms can use it in meetings to display financial dashboards on walls or tables.
This makes group discussions more interactive. It also eliminates the need for printed financial reports.
Superimposition AR
Superimposition AR replaces parts of the real world with digital overlays. In accounting, it can overlay financial metrics on top of physical documents.
This helps accountants quickly review and compare financial performance without switching between screens.
Outlining AR
Outlining AR highlights boundaries and structures in the physical world. While common in navigation, it also has accounting potential.
For example, it could outline organizational structures and link them to financial performance. This helps firms visualize where resources are most used.
Consequences of Augmented Reality in Accounting
Positive Impacts on Productivity
AR reduces time spent on manual data analysis and report preparation. Accountants can spend more time on advisory work and less on routine tasks.
This shift improves productivity across firms. It also raises service quality for clients.
Potential Risks and Drawbacks
Despite benefits, AR brings risks. High costs may limit adoption, especially for small firms. Technical issues can disrupt workflows if systems fail.
Additionally, reliance on AR may reduce traditional analytical skills. These skills remain valuable in accounting.
Ethical Considerations
AR can create ethical challenges. Firms must ensure data displayed through AR is accurate and not misleading.
If misused, AR visualizations might present overly optimistic scenarios. Accountants have a responsibility to maintain transparency when using such tools.
AR and Virtual Reality in Training and Development
Immersive Training for New Accountants
Traditional training relies on manuals and lectures. AR offers immersive experiences where trainees can simulate audits or tax planning.
This approach shortens the learning curve and improves retention of knowledge.
Ongoing Professional Development
AR also supports continuous learning. Accountants can access virtual workshops and interactive tutorials without leaving their office. Additionally, they can engage in scenario-based training remotely.
This ensures professionals stay updated on evolving regulations and accounting standards.
Cost Savings from Virtual Training Programs
Training costs can be high. AR and VR reduce the need for in-person sessions and printed materials.
By shifting to AR-based training, firms save money while still delivering quality education.
Real-World Examples of AR in Business and Accounting
AR in Global Audit Firms
Large firms like PwC and Deloitte have started experimenting with AR. They use it to visualize audit trails and simplify financial reviews.
These firms are investing heavily, signaling AR’s growing importance in the industry.
AR in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
SMEs are adopting AR at a slower pace due to cost concerns. But affordable cloud-based AR platforms are emerging, making adoption easier.
Some SMEs use AR dashboards to present financial performance to stakeholders. This improves clarity and trust.
Lessons from Early Adopters
Early adopters show that AR enhances both efficiency and client satisfaction. Firms that embraced AR reported faster audits and improved client relationships.
The lesson is clear: starting early offers a competitive edge in the accounting field.
Key Takeaways for Accountants and Firms
Why AR Adoption Matters
AR is not just a trend. It is becoming part of the digital transformation in accounting. Firms that ignore it risk falling behind competitors.
Adopting AR helps firms deliver more value to clients and streamline operations.
Strategies for Staying Ahead
Accountants should stay informed about AR developments. Attending industry events, investing in training, and testing AR tools can help prepare firms for the future.
Building partnerships with AR tech providers may also help ease integration challenges.
Preparing for the Next Wave of Technology
The next wave of accounting will combine AR with AI, blockchain, and cloud tools. Preparing now ensures firms remain competitive as the industry evolves. Accountants must be proactive rather than reactive when adopting new technologies.
Conclusion
Augmented reality (AR) is being increasingly equated with gaming or entertainment. It is changing how accountants process, report, and interpret financial data. AR brings real value to accounting. It allows reports to be viewed in three dimensions (3D). Additionally, it facilitates client consultation.
AR makes things more efficient, less error-prone, and easier to train. It also makes interactive financial reporting better and easier to understand. Cost, security issues, and reluctance to change are some of the hurdles. But early adopters will be much ahead.
For accountants, here’s a loud and clear message: AR is here to stay. Learning to take advantage will make you competitive in a fast-changing industry. As a large or small practice accountant, learning about AR can ensure your future.
FAQs
1. What are the 5 types of augmented reality?
The five types are marker-based, markerless, projection-based, superimposition, and outlining AR. Each serves different purposes, and all have potential in accounting.
2. What is augmented reality in banking?
In banking, AR improves customer service and helps with financial planning. Additionally, it supports risk management. It also connects with accounting by enabling real-time financial insights.
3. What is augmented reality, with examples?
Augmented reality overlays digital information onto the real world. For example, an accountant could project a client’s tax planning scenarios onto a table. This allows for easier comparison and discussion.
4. How is augmented reality used in business?
Businesses use AR for data visualization, employee training, customer engagement, and process optimization. In accounting, AR improves audits, reporting, and financial planning.
5. Why is augmented reality used in accounting?
AR makes accounting more accurate and efficient. It helps accountants visualize complex data, communicate with clients, and train staff effectively.
6. What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
AR is a technology that blends virtual elements with real-world environments. Unlike VR, which immerses you fully, AR enhances what you already see.
7. What are the consequences of augmented reality?
AR boosts productivity and efficiency, but it also raises challenges. Also, it includes high costs, technical barriers, and security risks if data is not protected.
8. How will virtual and augmented reality impact accounting and financial services?
They will transform financial services by making reporting interactive. This includes making audits more precise and strengthening client engagement. Firms that adopt early will set industry standards.






Leave A Comment